| diagram | 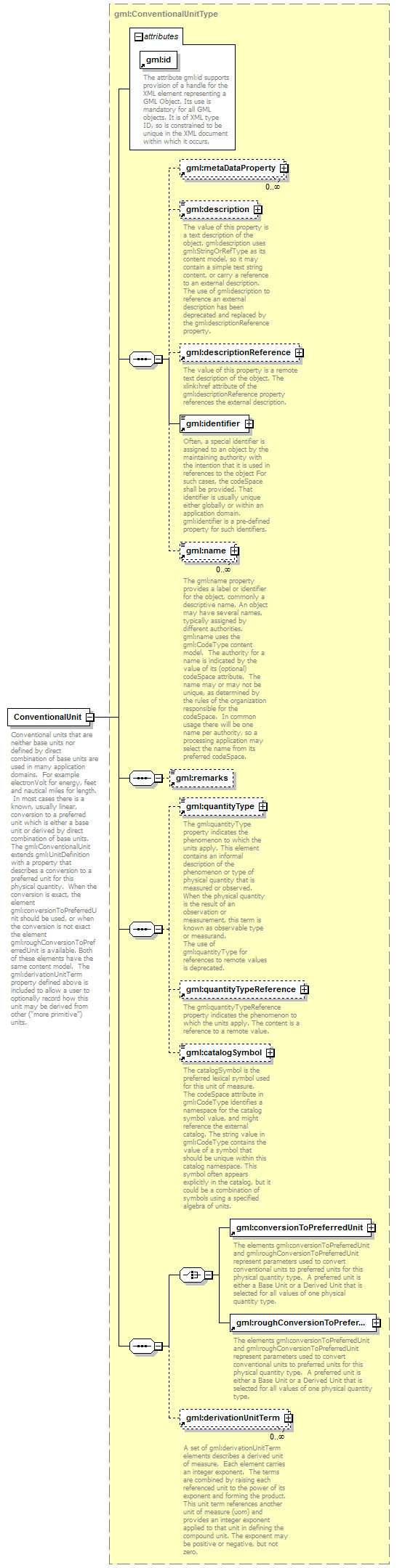 |
||||||||||||||
| namespace | http://www.opengis.net/gml/3.2 | ||||||||||||||
| type | gml:ConventionalUnitType | ||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||
| children | gml:metaDataProperty gml:description gml:descriptionReference gml:identifier gml:name gml:remarks gml:quantityType gml:quantityTypeReference gml:catalogSymbol gml:conversionToPreferredUnit gml:roughConversionToPreferredUnit gml:derivationUnitTerm | ||||||||||||||
| attributes |
|
||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||
| source | <element name="ConventionalUnit" type="gml:ConventionalUnitType" substitutionGroup="gml:UnitDefinition"> <annotation> <documentation>Conventional units that are neither base units nor defined by direct combination of base units are used in many application domains. For example electronVolt for energy, feet and nautical miles for length. In most cases there is a known, usually linear, conversion to a preferred unit which is either a base unit or derived by direct combination of base units. The gml:ConventionalUnit extends gml:UnitDefinition with a property that describes a conversion to a preferred unit for this physical quantity. When the conversion is exact, the element gml:conversionToPreferredUnit should be used, or when the conversion is not exact the element gml:roughConversionToPreferredUnit is available. Both of these elements have the same content model. The gml:derivationUnitTerm property defined above is included to allow a user to optionally record how this unit may be derived from other ("more primitive") units.</documentation> </annotation> </element> |
XML Schema documentation generated by XMLSpy Schema Editor http://www.altova.com/xmlspy